Understanding the Roles in Participant Directed Services (PDS): Why Community Guides Matter
When navigating Participant Directed Services (PDS), understanding the distinct roles of each team member is key to ensuring effective support and compliance. One common misconception is that Community Guides (CGs) simply duplicate the role of a participant’s representative - but in reality, CGs provide specialized support that enhances the success of self-direction.
Additionally, the distinction between an employer and a human resources (HR) department can help clarify why CGs are an essential service. Let’s break it all down.
Who's Who in PDS?
Case Managers (CMs)
Case Managers act as coordinators, ensuring that individuals receiving waiver services are accessing appropriate supports. Their primary role is to monitor the health, safety, and welfare of participants. They help develop and monitor person-centered plans, ensure compliance with Medicaid requirements, and facilitate access to resources. However, they are not directly involved in the day-to-day employer responsibilities within PDS.
Community Guides (CGs)
Community Guides are a separate service designed to help participants successfully manage their self-directed services. They provide training and ongoing support to ensure participants (or their representatives) understand employer responsibilities, Medicaid requirements, and best practices for hiring and managing staff.
CGs are particularly valuable for individuals who are new to self-direction, those facing challenges in managing their services, or families who need assistance navigating the complexities of being an employer.
Currently, CG services are only available as a separate billable service through the Supports for Community Living (SCL) waiver. However, individuals on other waivers - such as the Michelle P. (MPW) and Home and Community Based (HCB) waivers - could also benefit significantly from this structure and support. While CG services technically exist under the MPW waiver, they can count against the 40-hour weekly service limit for participants, which limits access. Expanding CG availability across waivers would help ensure more individuals can successfully manage their services without sacrificing other critical supports.
Participants & Representatives
Participants are individuals who are receiving services through a Medicaid waiver. If a participant is unable to manage their services independently, they may appoint a representative - often a family member or trusted person - to act on their behalf in making employment-related decisions. Representatives play a vital role in supporting the participant’s goals and preferences while ensuring that services remain compliant and effective. They are responsible for approving employee timesheets and service documents and making the decisions regarding the hiring and firing of employees.
While participants and representatives can handle employer-related tasks, the role of a CG is to provide expert guidance, ensure compliance, and offer ongoing support to enhance the experience with self-direction and overall independence.
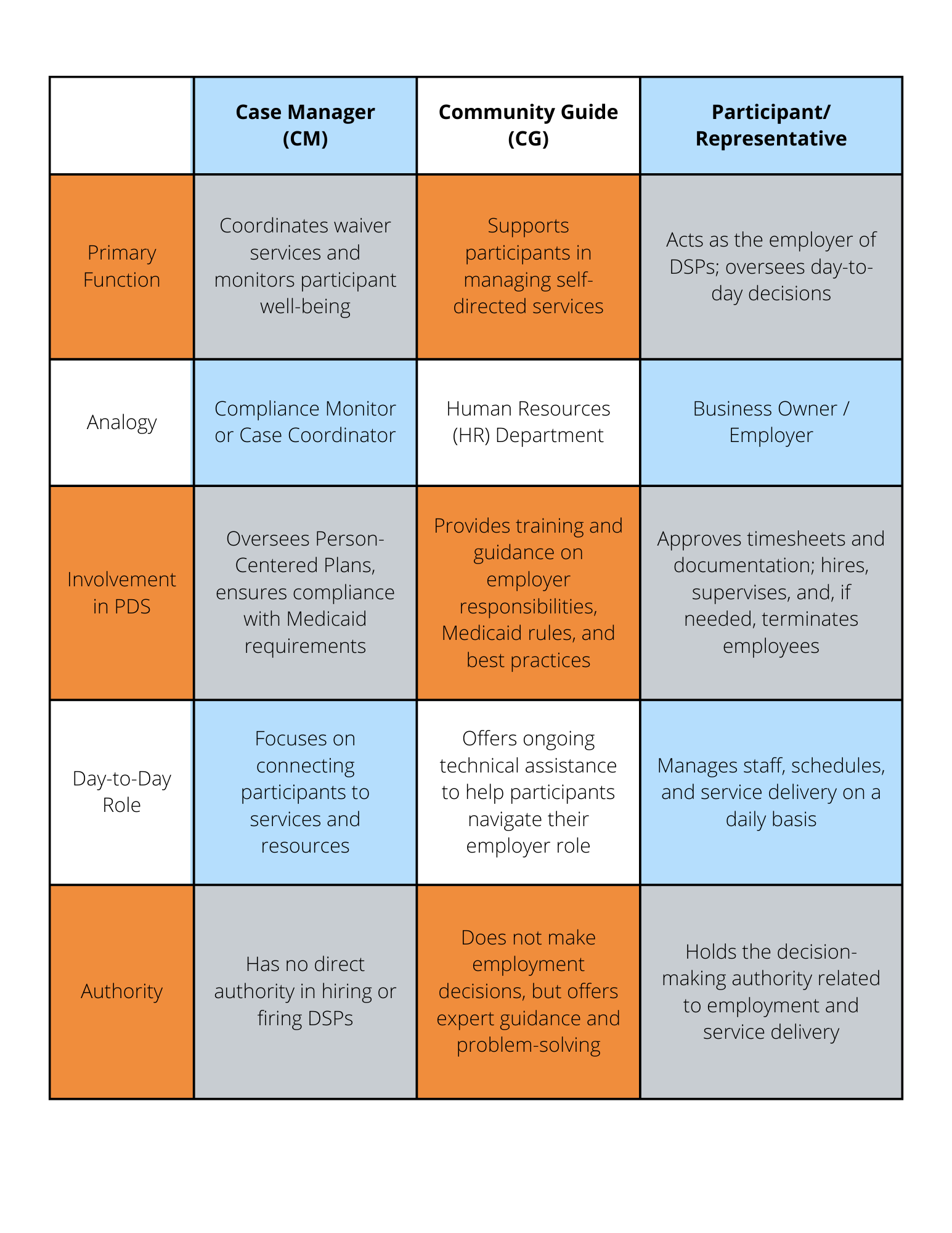
Employer vs. HR Department: Why Both Are Necessary
A helpful analogy to understand the role of CGs is comparing an employer to a business owner and CGs to a human resources (HR) department.
- Employers (Participants/Representatives) make hiring decisions, oversee employee performance, and manage the daily operations of their self-directed services.
- HR Departments (Community Guides) provide training, guidance, and policy support to ensure employers are in compliance with labor laws, Medicaid regulations, and best practices in hiring and staff management.
Just like a business owner might know how to hire and supervise staff, they still rely on an HR department for expertise in policies, compliance, and best practices. The employer holds the power to make the decisions, but the HR department ensures that power is exercised effectively and legally. The relationship is the same between CGs and participants/representatives. CGs provide that layer of support within PDS, ensuring that participants can navigate self-direction successfully.
What's Next?
To ensure that the valuable Community Guide service remains available, it’s important that state policymakers and administrators understand the value that CG services provide. CGs are more than just "paid representatives" - they are a crucial support that helps individuals with disabilities successfully navigate self-direction. By clarifying these roles and advocating for continued and expanded CG services, we can ensure that participants receive the guidance they need to live independently, with dignity, and make their own decisions.
Sustaining and expanding Community Guide services requires a shared commitment to education, advocacy, and collaboration. By correcting misconceptions, highlighting real-world success stories, and learning from other states’ self-direction models, we can secure CGs as a cornerstone of high-quality, person-centered care. Let’s ensure that every participant - regardless of waiver type - has the support they need to thrive in self-direction!
